What Is a Supply Chain Attack?

In our increasingly interconnected world, supply chain attacks have emerged as one of the most concerning cybersecurity threats. But what exactly is a supply chain attack? In this post, we’ll break it down, explore real-life examples, and discuss how you can protect your organization from this insidious threat.
What Is a Supply Chain Attack?
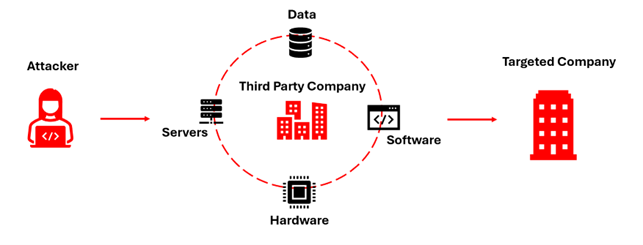
A supply chain attack occurs when cybercriminals target an organization by infiltrating its supply chain or the networks and software used by that organization. Instead of attacking the primary target directly, hackers compromise a third-party vendor or software provider to gain access to sensitive information or systems.
Why Are Supply Chain Attacks So Effective?
Supply chain attacks have become a favored tactic among cybercriminals and adversaries due to their cunning nature and potential for widespread impact.
According to recent estimates, 2769 entities were targeted with a supply chain attack in 2023. The average cost of a supply chain attack is $4.46M and requires on average 26 days to identify and contain. A supply chain attack is therefore almost as expensive as an average single data breach, which costs companies around $4.88 million in 2024.
By targeting the connections and relationships between organizations and their vendors, attackers can exploit vulnerabilities that are often overlooked. In this section, we’ll explore the reasons these attacks are so successful and why organizations need to be particularly vigilant about their supply chains.
- Trust Relationships: Organizations often trust their suppliers and vendors, making it easier for attackers to gain access.
- Complex Networks: Modern supply chains can be intricate, involving multiple vendors, making it challenging to identify vulnerabilities.
- Difficult to Detect: These attacks can go unnoticed for extended periods, allowing attackers to gather data and execute further malicious activities.
Real-Life Examples of Supply Chain Attacks
To truly understand the severity of supply chain attacks, it’s essential to look at real-world incidents that have had profound implications for organizations and individuals alike. These examples highlight not only the methods employed by cybercriminals but also the far-reaching consequences of such breaches.
Let’s delve into some notable supply chain attacks that have shaped the cybersecurity landscape and underscored the critical need for robust security measures.
1. SolarWinds (2020)
One of the most significant supply chain attacks in recent history was the SolarWinds incident. Here’s how it unfolded:
- Target: SolarWinds, a major IT management company.
- Attack Method: Hackers infiltrated SolarWinds’ software updates, inserting malicious code into their Orion software platform.
- Impact: This compromised thousands of organizations, including U.S. government agencies and Fortune 500 companies, allowing attackers to spy on sensitive data for months undetected.
This attack highlighted the vulnerability of third-party software providers and the extensive reach such an infiltration could have.
2. Target (2013)
The Target data breach is another prime example:
- Target: The well-known retail giant.
- Attack Method: Attackers gained access through a third-party vendor, Fazio Mechanical Services, which provided HVAC services.
- Impact: The breach resulted in the theft of 40 million credit and debit card numbers and the personal information of 70 million customers.
Target’s case illustrates how even seemingly unrelated vendors can become gateways for cybercriminals.
3. Attack on Hezbollah Pagers (2024)
In September 2024, Israel conducted a sophisticated operation against Hezbollah, a militant group based in Lebanon, showcasing a unique form of supply chain attack:
- Target: Hezbollah, a key adversary of Israel.
- Attack Method: Israeli operatives concealed explosives within the batteries of pagers brought into Lebanon. This clever tactic exploited the trust associated with everyday devices to deliver a deadly payload.
- Impact: The operation showed how attackers can use supply chains to sneak dangerous items into places, getting around regular security checks. This incident not only highlighted the changing nature of conflicts but also raised serious worries about the safety of everyday electronic devices and the possibility of similar tactics being used in the future.
This attack shows that supply chain weaknesses can affect not just cybersecurity but also physical security and international relations. It highlights the importance of being cautious in both areas.
How to Protect Your Organization from Supply Chain Attacks
While supply chain attacks can be difficult to prevent, there are several steps you can take to strengthen your defenses:
1. Conduct Risk Assessments
- Regularly evaluate the security practices of your suppliers and vendors.
- Identify critical suppliers that have access to sensitive information.
2. Establish Strong Vendor Management Policies
- Ensure that all third-party vendors comply with your organization’s security standards.
- Implement contractual obligations that require vendors to maintain specific cybersecurity measures.
3. Monitor and Audit Supply Chain Security
- Continuously monitor your supply chain for any unusual activity.
- Conduct regular audits to ensure compliance with security protocols.
4. Implement a Zero-Trust Model
- Adopt a zero-trust approach, meaning no one is trusted by default, even if they are within the organization’s network.
- Verify every user and device before granting access to sensitive information.
5. Enhance Employee Training
- Train employees to recognize potential supply chain risks and report any suspicious activity.
- Promote a culture of security awareness within your organization.
Conclusion
Supply chain attacks represent a significant and growing threat in today’s cybersecurity landscape. By understanding what these attacks are and how they can occur, organizations can take proactive steps to safeguard themselves against this hidden menace.
In a world where every link in the chain can be a potential vulnerability, vigilance and collaboration with trusted partners are essential. By implementing robust security measures and maintaining strong relationships with vendors, organizations can significantly reduce their risk and protect their sensitive data from cybercriminals.