Protected Management Frames (PMF)

Understanding Protected Management Frames (PMF): Enhancing Wi-Fi Security
Wi-Fi security has evolved significantly over the years, and one key advancement is the introduction of Protected Management Frames (PMF) in the IEEE 802.11w amendment. Protected Management Frames is a crucial feature designed to enhance the resilience of Wi-Fi networks against various attacks, including deauthentication and disassociation attacks. In this blog, we’ll explore what PMF is, why it matters, and how you can enable and verify it on your network.
What Are Management Frames in Wi-Fi?
Wi-Fi networks rely on management frames to handle communication between devices and access points (APs). These frames coordinate tasks such as:
- Joining and leaving a network.
- Authenticating and associating devices.
- Handshaking and roaming.
Unfortunately, these frames were traditionally sent unencrypted, making them vulnerable to spoofing and injection attacks. For example, an attacker could send deauthentication frames, forcing devices to disconnect from the network, paving the way for attacks like Evil Twin and Wi-Fi jamming.
What Is Protected Management Frames (PMF)?
PMF secures management frames by encrypting and authenticating them, ensuring they cannot be spoofed or tampered with. Introduced in the 802.11w amendment, PMF is now mandatory for devices supporting WPA3, and optional for WPA2.
Key Features of PMF:
- Encryption: Management frames are encrypted, protecting against eavesdropping.
- Authentication: Frames are validated, preventing spoofing and tampering.
- Backward Compatibility: PMF can operate in mixed environments where some devices do not support it.
PMF has three operational modes:
- Disabled: PMF is not enforced.
- Capable: PMF is enabled but not mandatory; devices can connect even if they don’t support PMF.
- Required: PMF is enforced, and only PMF-capable devices can connect.
Why Is PMF Important?
PMF defends against two critical types of attacks:
- Deauthentication and Disassociation Attacks: These attacks disconnect users from the Wi-Fi network by spoofing management frames.
- Broadcast Deauthentication Attacks: Attackers target multiple devices simultaneously to cause widespread disconnection.
By enabling PMF, you ensure that your Wi-Fi network is more secure and resilient against such attacks.
How to Enable PMF on Your Network
Enabling PMF varies based on the router or access point you are using. Below are general steps to enable it on popular platforms:
1. Enable PMF on a Home Router
Most modern routers support PMF. Here’s how to enable it:
- Access your router’s admin panel:
- Open a web browser and navigate to your router’s IP address (e.g.,
192.168.0.1or192.168.1.1). - Log in with your admin credentials.
- Open a web browser and navigate to your router’s IP address (e.g.,
- Find the Wi-Fi settings:
- Navigate to the wireless security section (often labeled “Wireless,” “Wi-Fi Settings,” or “Advanced Settings”).
- Enable PMF:
- Look for an option like Protected Management Frames or 802.11w.
- Choose “Capable” (to allow all devices to connect) or “Required” (to enforce PMF).
- Save the settings and reboot the router.
2. Enable PMF on Enterprise Networks
For enterprise-grade networks using platforms like Cisco, Aruba, or Ubiquiti:
- Access the network management interface (via web UI or command line).
- Locate the wireless security settings for the SSID.
- Configure PMF to be “Optional” (Capable) or “Mandatory” (Required).
- Apply the changes and ensure all connected devices support PMF.
How to Verify PMF with Wireshark
To confirm whether PMF is enabled on your network, you can use Wireshark, a powerful packet capture tool. Follow these steps:
Step 1: Set Up Wireshark
- Install Wireshark:
- On Linux:
sudo apt install wireshark - On Windows or macOS: Download from Wireshark’s official website.
- On Linux:
- Open Wireshark and select your Wi-Fi interface for capturing packets.
Step 2: Capture Management Frames
- Ensure your network card is in Monitor Mode:
- On Linux: Use
airmon-ngto enable monitorsudo airmon-ng start wlan0 - On Windows: Use a compatible Wi-Fi adapter.
- On Linux: Use
- Start capturing packets in Wireshark:
- Apply a filter to focus on management frames:
wlan.fc.type_subtype == 0x0c || wlan.fc.type_subtype == 0x0a- 0x0c: Deauthentication frames.
- 0x0a: Disassociation frames.
- Apply a filter to focus on management frames:
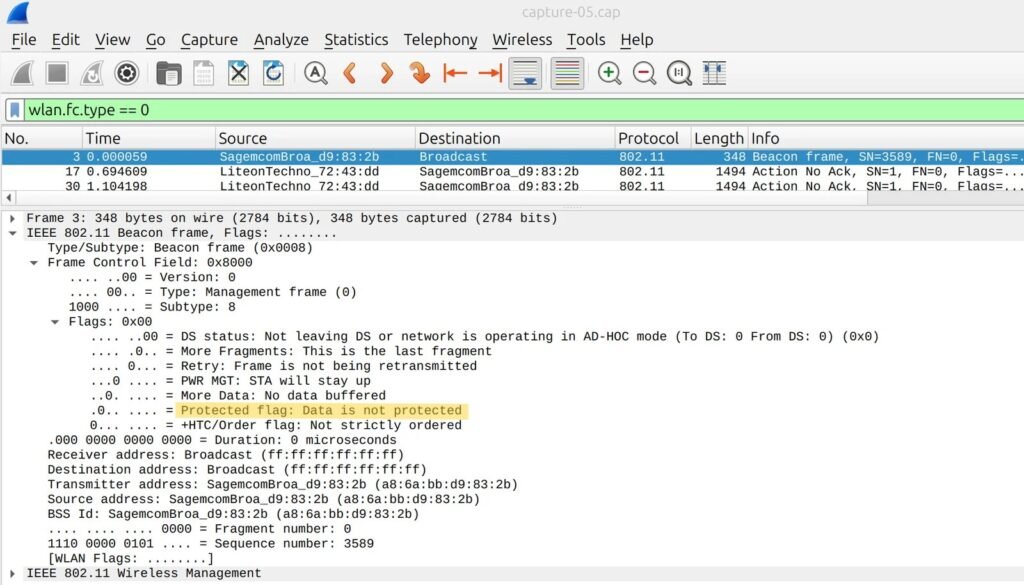
Step 3: Analyze the Frames
- Look at the “Frame Control” field in the captured packets.
- Check for the presence of the Protected bit:
- In protected management frames, the “Protected” field will be set to
1, indicating that PMF is in use.
- In protected management frames, the “Protected” field will be set to
- If the “Protected” bit is
0, PMF is not enabled.
Step 4: Test with Deauthentication
- Use a tool like
aireplay-ng(in a controlled lab environment) to send deauthentication packets to a device. - Observe if the device disconnects:
- If PMF is enabled, the attack will fail, and the device will remain connected.
Conclusion
Protected Management Frames (PMF) is a vital feature for modern Wi-Fi security, protecting against spoofing and deauthentication attacks. By enabling PMF on your network, you add an essential layer of security, ensuring that your devices remain connected and secure.
Whether you are a home user or managing an enterprise network, enabling PMF is straightforward and worth the effort. Don’t forget to verify it with Wireshark to ensure it’s functioning as expected!
By following this guide, you can secure your Wi-Fi network with PMF and better understand its importance in combating Wi-Fi attacks. Let me know in the comments if you have questions or need further assistance!